
The importance of e-commerce SEO
The importance of e-commerce SEO best practices shouldn’t be underestimated. SEO for e-commerce websites is something where many online stores are failing miserably, unable to fully exploit the power of organic marketing.
Ranking at the top of search engines is a high priority. While paid search can place you at the top of the SERPs you there, the long-term cost to remain there may not be sustainable. You need the number one spot, and e-commerce SEO can help you achieve this.
What is E-commerce SEO?

Ecommerce SEO is the process of making your online store more visible in the search engine results pages (SERPs). When people search for products that you sell, you want to rank as highly as possible so you get more traffic.
Ecommerce SEO usually involves optimizing your headlines, product descriptions, meta data, internal link structure, and navigational structure for search and user experience. Each product you sell should have a dedicated page designed to draw traffic from search engines.
Why SEO For Ecommerce Matters?
Let’s quickly look at some interesting stats…
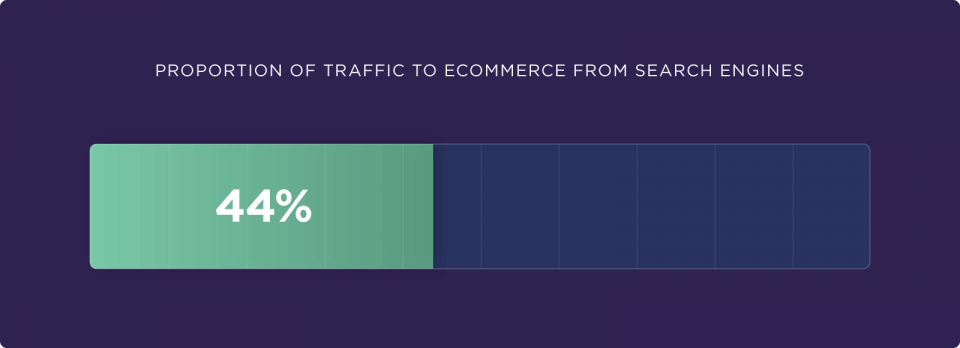
44% of people start their online shopping journey with a Google search (nChannel).
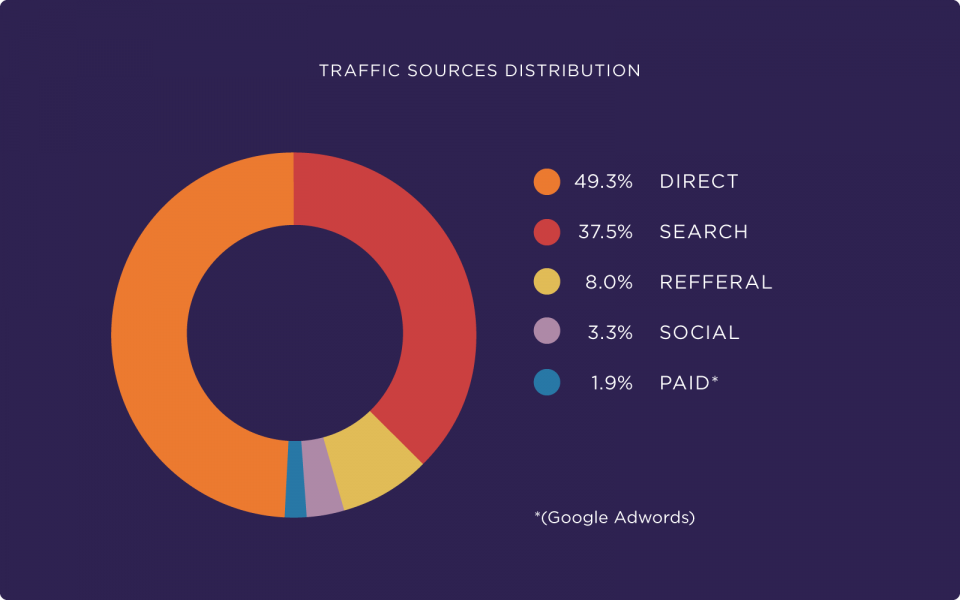
37.5% of all traffic to ecommerce sites comes from search engines (SEMrush).
23.6% of ecommerce orders are directly tied to organic traffic (Business Insider).

Key Tactics to Include in Your Ecommerce SEO Strategy
The best ecommerce SEO strategy includes:
- Keyword research to find the types of keywords customers are searching.
- Site architecture based on your keyword research.
- On-Page SEO through strategic keyword optimization in meta tags and content.
- Technical SEO to help ensure search engines can crawl your site efficiently.
- Local SEO to help drive local organic traffic (if you have a brick and mortar).
- Content marketing to drive additional organic visitors.
- Link Building to help improve the authority of your website.
- Measuring SEO Success with tools like Google Analytics and Ahrefs.
E–commerce Keyword Research
Most keyword research tutorials focus on “informational keywords”.
While informational keywords have their place in ecommerce, the majority of site’s keywords will be tailored around product searches.
That means that we need to tackle keyword research with product-focused keywords in mind.
how to perform ecommerce keyword research, find keyword difficulty (KD) and search volume, and uncover buyer intent?
Well, there are three ways:
1. Use Amazon for keyword research
People literally search on Amazon with the intent of buying something.
To find keywords with Amazon, start typing in your seed keyword. This is a word you think you’d probably like to rank for.
For example, we could type “washing”
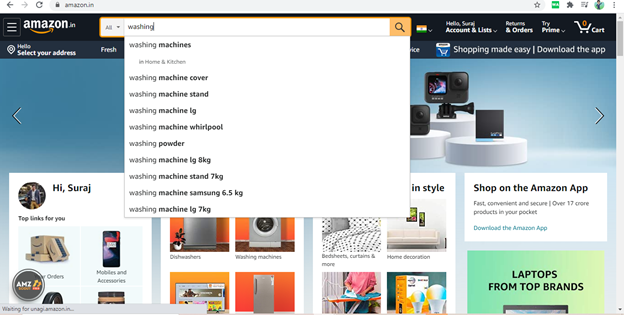
and Amazon spits out autofill suggestions like washing Machine, washing Machine cover, washing Machine stand, etc. These are all keyword ideas.
As you can imagine, if you have hundreds or thousands of products, this could take a long time. That’s where the Amazon Keyword Tool comes in.
2. Find keywords through competitor research.
If you have competitors who rank higher than you in search results, you can use their site to steal keyword ideas.
First, type your keyword into Google…
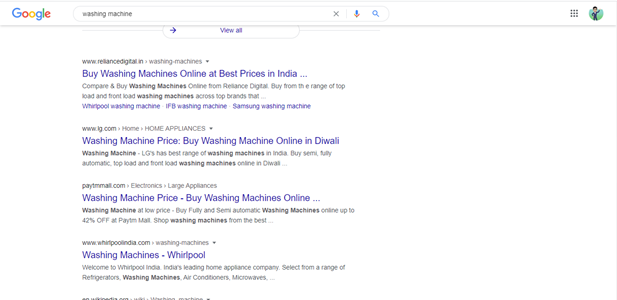
choose a competitor and scan their category and product pages for potential keywords.
However, do NOT blindly use the same keywords as your competitor! Just because they outrank you, doesn’t mean they’ve chosen the best keywords — they could just have a higher domain authority (DA)
3. Use Ahrefs to help you find keyword opportunities
Ahrefs, the tool I mentioned above, is an all-around amazing SEO tool. You can use it for keyword research, competitive research, to build backlinks and much more.
And we’ll get to all that, but for now let’s talk about how to use it to perform ecommerce keyword research easily and quickly.
4. Determine if you are choosing the right keywords.
Unless you used Ahrefs, you won’t have keyword data for the phrases you picked. You need to determine keyword difficulty, search volume and buyer intent to know which keywords to use.
You can find rough search volume and CPC (to determine buyer intent) using Google Keyword Planner. However, it doesn’t give you keyword difficulty (don’t be confused by competition — that’s just competition for paid AdWords ads, not organic ranking).
A keyword matrix is basically a way to dig through all your keywords and organize your spreadsheet to quickly determine the best possible keywords to use on each of your pages. It’s based on KD, search volume and search intent (what people are looking for when they make a particular search).
If that’s something you’re interested in, you can read more about it . hire me to do it for you.
Ecommerce Site Architecture
Great architecture can dramatically affect your website’s usability, rankings, and conversions. In addition, proper planning will make expanding your product lines in the future a breeze. This is especially true with e-commerce websites because of the sheer size of the website.
Focus on creating a “flat architecture” for your website, meaning design that requires as few clicks as possible to go from your home page to your product page. This way, the maximum amount of “link juice,” or authority, will pass from your home page to your product page via internal links.
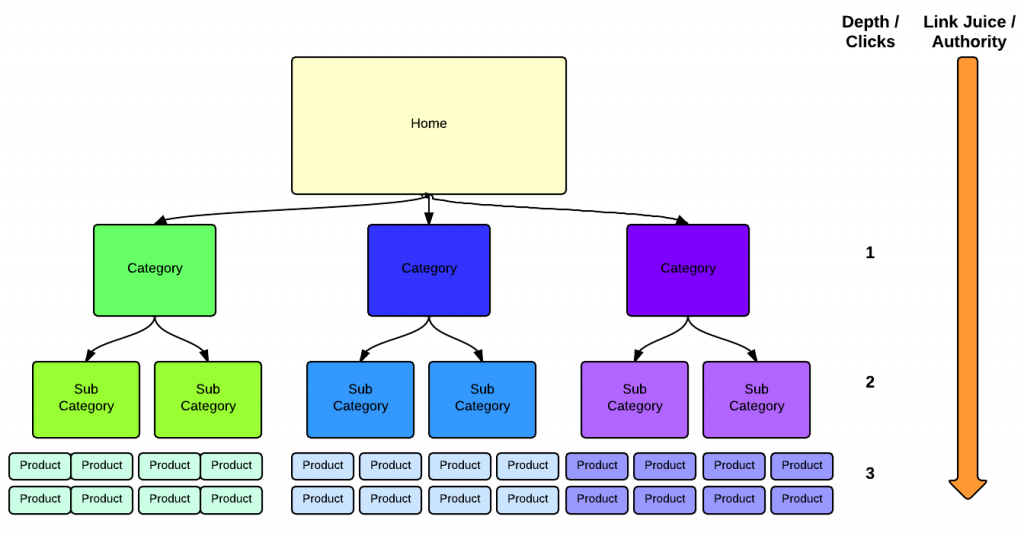
The layout illustrated above obviously has links from the home page down to the product page. It’s also helpful to link between pages and categories to distribute “link juice” to pages that have a higher priority for ranking.
An On-Page SEO Strategy for Ecommerce Sites
On-page SEO for ecommerce is all about making sure your keywords are in the right places. It’s just a way of ensuring Google knows exactly what your page is about.
We’re about to discuss three strategies:
- On-page SEO for eCommerce category pages.
- On-page SEO for eCommerce product pages.
- On-page SEO for your blog content.
On-page SEO is important because it also helps you appear in other Search Engine Results Page (SERP) features.
How to optimize your category pages
- Optimize your Category URLS – Keep your URLs clean, short and to the point and make sure that the user can tell from the URL alone what the category is all about.
- Optimize your Category titles – Use specific characteristics of the category products in the title. For example, if you have a category page with green athletic shoes, make sure that this is reflected in the title as welle. “Green Athletic Shoes – Discounts available for bulk purchases”.
- Optimize your Category META description: In your category descriptions try to summarize your products and offerings. If you offer free shipping, free returns etc. say so in the description to encourage users to click on your entry.
- Category H1 tag: The category page should have only one H1 tag and this should be on top of the page. It can be the same as the TITLE of the page or different, but it should still contain your target keywords.
- Category Text Content: A good way to overcome this problem is to have a few lines of content below the H1 tag and then add some related text content at the bottom of the page.
- Conversion Optimization Elements: If you have a lot of products in your category pages, make it easier for users to find what they want by showing them a list of the most popular (or best selling) categories and products.
- Visual Components and Other Usability Elements: Besides displaying the right content, a properly optimized category page should also include images and other elements to help users find what they want in the least possible number of clicks.
- Set the Canonical URLs Correctly: To make sure that Google will understand that the subsequent pages are part of the main category page, you need to set the canonical URL for the other pages to https://www.example.com/my-product-category.
Conclusion.
Category pages are important for ecommerce websites. It is vital to understand that you don’t have any choice when it comes to SEO optimizing your category pages.
Properly optimized category pages can help your shop achieve better rankings in search while non-optimized pages can generate the opposite results.
In summary, an SEO optimized category pages should:
- Have an SEO friendly URL that describes the category
- A title that includes keywords related to the products in the category
- A well-crafted description that gives users enough information as to why they should click your link from the SERPS.
- A unique H1 tag (with keywords)
- Text content that includes relevant information about the category and internal links to subcategories or other pages of the website.
- High-quality images of the products (or subcategories)
- Filters and other features to help users narrow down their selection and find what they want in the fastest possible way
- Incorporate all conversion optimization elements like your store’s homepage (offers, customer reviews, call to action buttons etc.)
- Set the canonical URL correctly so that there are no issues with lost backlinks or duplicate content.
